Brochure
Prezi Presentation
How and When Did Switzerland Become So Rich?
Switzerland (or Helvetia, the original name of the state)i s one of the most unique and stunning places on the entire world. It is a mountainous and landlocked country located in Western and Central Europe. Administrative capital of Switzerland is Bern and Lausanne is its judicial center. In spite of its small size ( approximate half of the Scotland territory) and its low political activity, Switzerland has a very high level of life.
If somebody would ask you what you know about this coveted country, your answer would be probably related on these themes: safe and reliable banks, delicious chocolate and cheese, prosperity and stability. Moreover, it is kind of impossible to find anything negative about Switzerland in the news and the reason for this is that Swiss Republic never takes part in wars and has a very low level of criminality. But, how did this country manage to obtain such a high status? To answer to this question we should take a look over the geography and history of Switzerland.
As we already know, it is situated in Western and Central Europe. It comprises the Alps, many forests, lakes, waterfalls and it has temperate continental climate. All these factors positively affect the attractiveness of Switzerland for tourists and as a consequence, the economical growth of the state.
Now let’s move on to the history of this astonishing country. In 1815, a significant decision was made – Vienna Congress confirmed the neutrality of Switzerland. Since then , Switzerland never took part in any war, though it always had the required arms to protect itself. In addition to this, none of its banks was ever robbed. Security of costs and keeping of banking secrecy made Switzerland the most popular state among foreigners for depositing money. As a matter of fact, from baking fees Switzerland gets huge amounts of money.
Therefore, the answer for the question “How and when did Switzerland become so rich?” stays in its favorable geographical position and in its history when its neutrality was confirmed by the Vienna Congress in 1815. These two key factors led to growth and prosperity for the modern Switzerland.
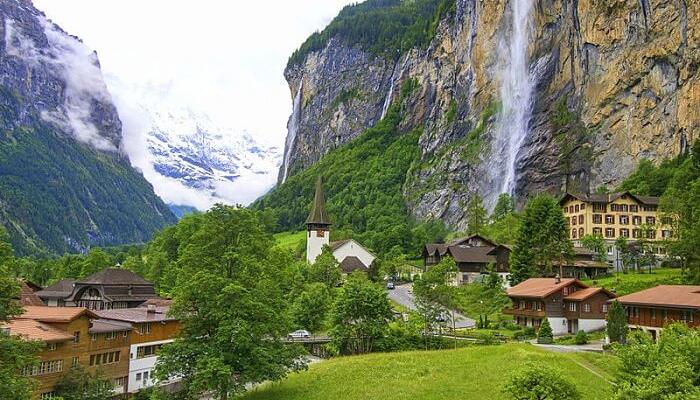

Staubbach Falls, Lauterbrunnen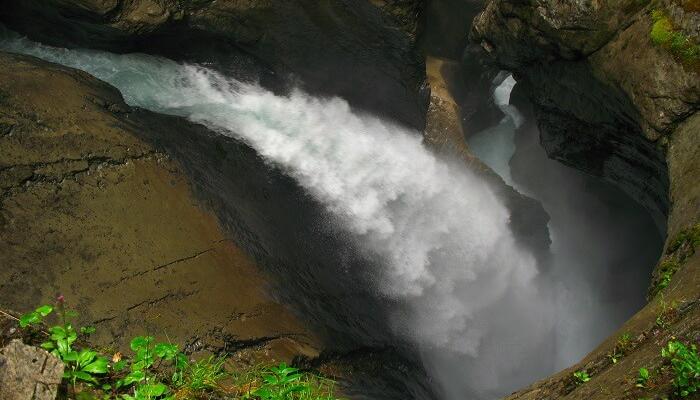 
Trümmelbach Falls, Lauterbrunnen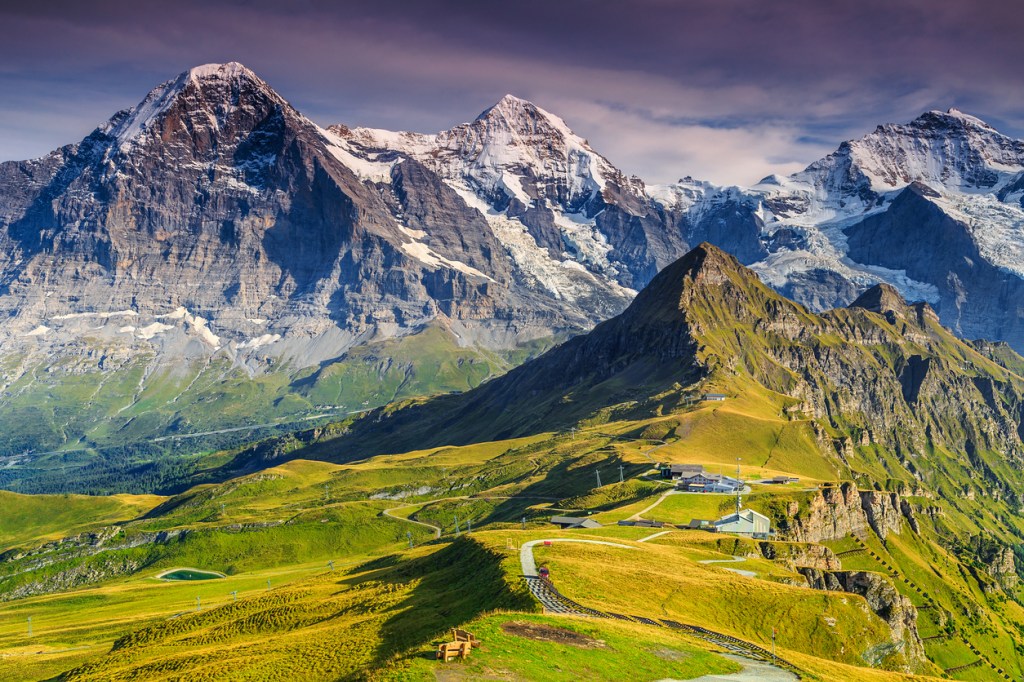 
SWISS ALPS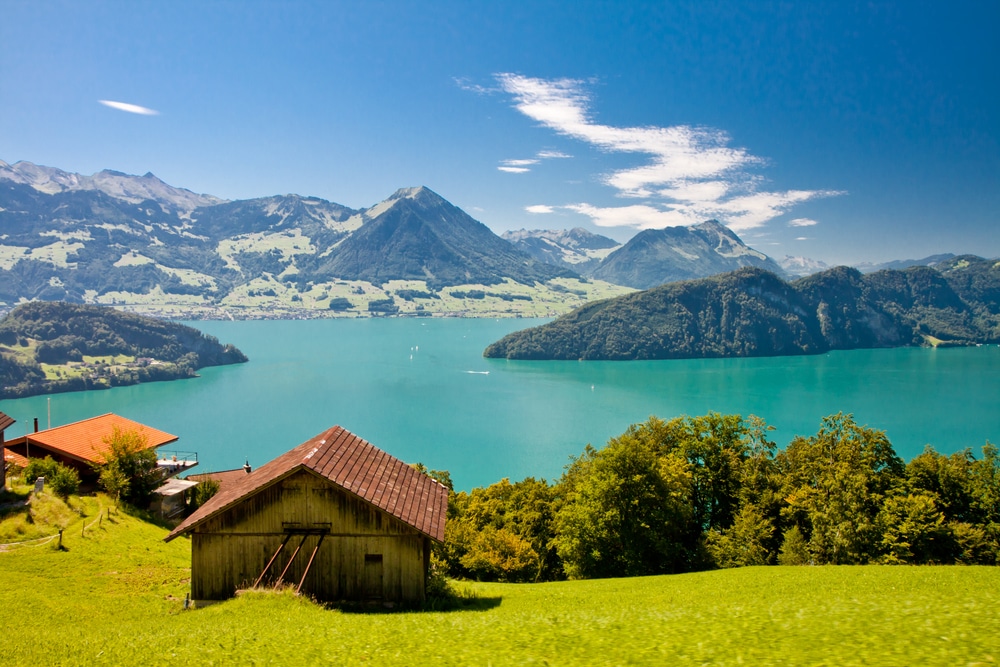 
Lake Lucerne; Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden & Lucerne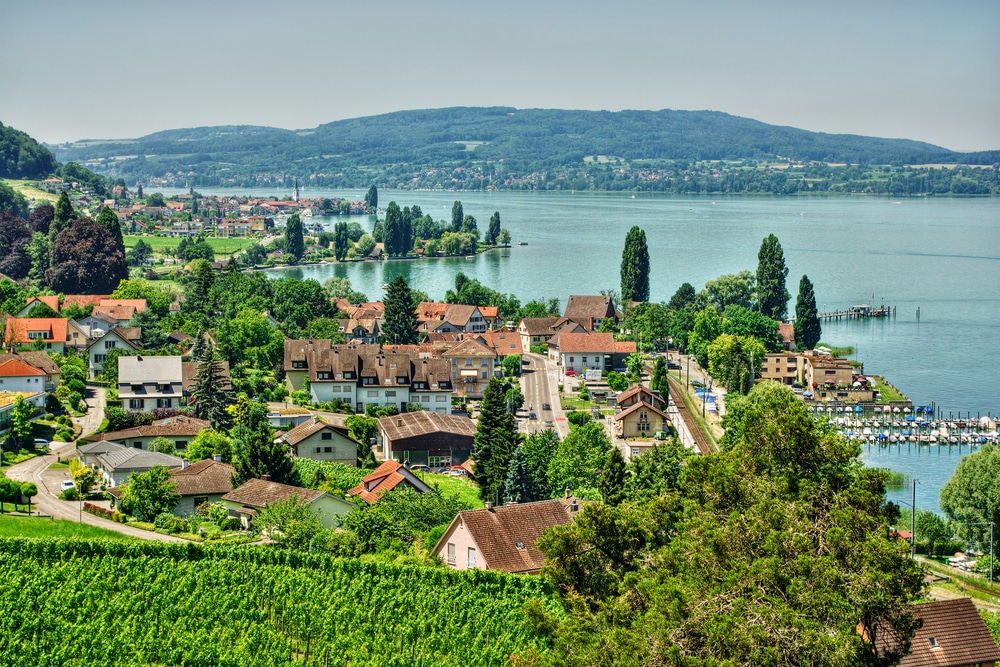 
Lake Constance; Thurgau, St. Gallen & Schaffhausen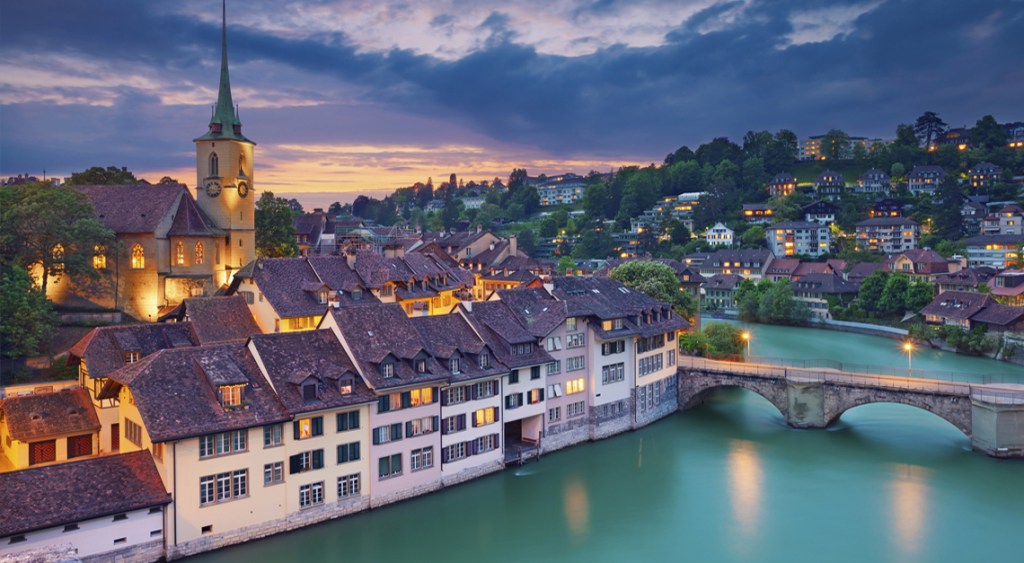 
BERN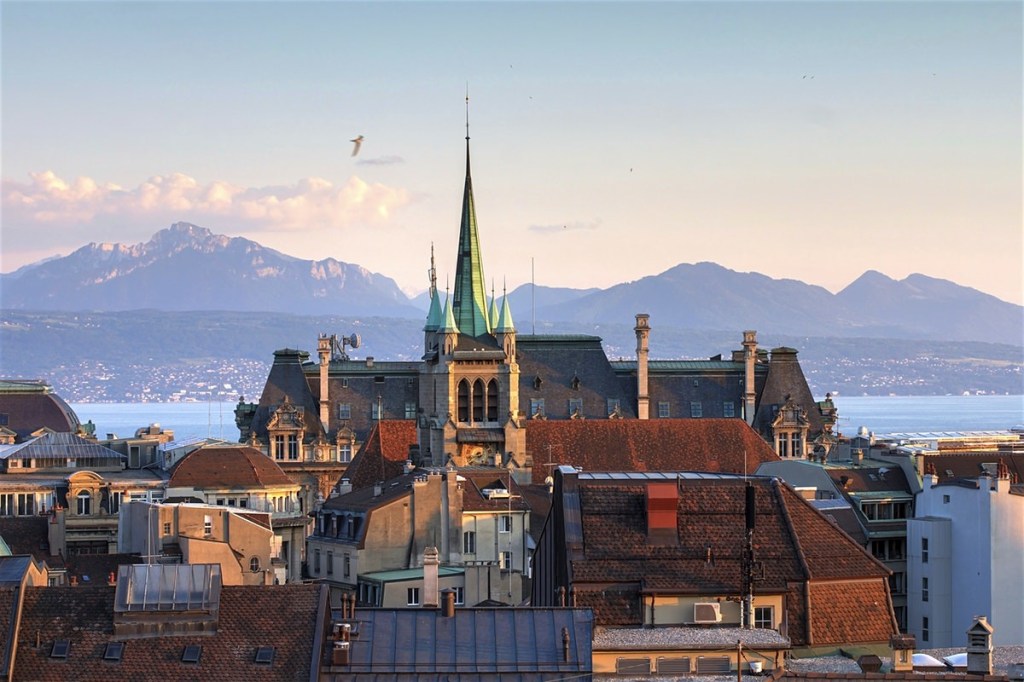
Lausanne
China and Hong Kong as a Whole
The economics of Hong Kong and Chinese mainland are, in fact, pretty much different in this field. China operates as a socialist market economy, which is characterized by state-owned enterprises and public ownership within a market economy. On the other side, because of its low taxation and free markets, Hong Kong’s economy is considered as one of the most liberal.
It is no surprise that, nowadays, China is the biggest producer of the majority of industrial products and the world’s largest exporter. Over the last two decades, China has become the supplier for many others countries and its ascension, most probably, will not get to an end in the near future.
At the present time, Hong Kong and Chinese mainland are in the framework of “one country, two systems”. In conformity with this approach the Central People’s Government is responsible for foreign policy and for the defense of territory of Hong Kong. Even if Hong Kong has all the power over of legislative self-control, taxes, monetary system and duties, Chinese mainland plays an important role in numerous integrative processes between it and Hong Kong. Up to this day, the signing of CEPA parties in 2003 was the most momentous attainment in this area. It quickly became the main instrument of intensification of the integration process between Hong Kong and Chinese mainland.
The costs of good imports from Hong Kong to the mainland is reduced by the CEPA’s policy which consist in applying zero tariffs. In this way, the competitiveness of these products is enhanced and the growth of exports of Hong Kong to the mainland is stimulated.
As well, CEPA contributes to the process of the production division between Hong Kong and mainland China. With the support of the CEPA , the high-tech industries in Hong Kong will have a faster development and in the meantime, China will use its advantage in labor-intensive production, mostly in those that are subject to market changes. For instance, if some enterprises of mainland China will transfer parts of its manufacturing to Hong Kong, they could avoid the policy of discrimination and safeguard of the West against Chinese goods.
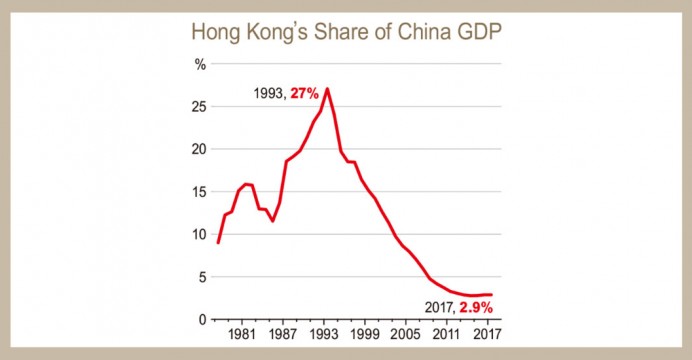
With no doubt, both sides can merge their advantages, so that Hong Kong should provide high-quality services for the manufacturing area in mainland China, thus enhancing the overall competitiveness of the Chinese economy.
